|
December 22, 2025
Spark Gap Video Editor for FFmpegThe Zippy Clipper Full Distro Full Installation The most reliable way to install on a Debian-based system is to download and decompress the distro file file (see below) onto your desktop and compile and build the system in its entirety. This should eliminate any library issues which sometimes occur. To do this, from the sgr-player directory, do the following:
sudo ./DebInstall.script The first script will download and install system libraries needed by the compile. It will take sometime to execute and produce many messages. The second command configures the source code to your system. The third command compiles the code (hint: add -j X at the end of the make where X is the number of CPUs you have - this will make the compilation run quicker). The third command installs the package on your system. You my now run it with the command: sgr-player Installers Specific installers for specific versions of Linux appear below. Installers are much smaller and quicker than the full install as shown above. Note: you may see messages saying some software is missging after you run the dpkg command below. The second command, the apt command, should correct these issues. You should update your installation cache before installing: sudo apt update Also, be sure that Update Manager is not running at the same time as it will interfere with these installers. To use an installer to install, download the installer for your version of Linux and, from a terminal window, type the following:
sudo dpkg --install sgr-zippy-amd64-VERSION.deb Where VERSION describes the version of Linux you are using. The second command will install from standard system repositories any missing packages needed to run the sgr-player code. Do not be suprised if on most systems, many packages will be installed.
Ubuntu 25.10 Installer:
sgr-player-amd64-zippy-25.10.deb
Linux Mint 22.2 Installer:
sgr-zippy-amd64-mint-22.2.deb
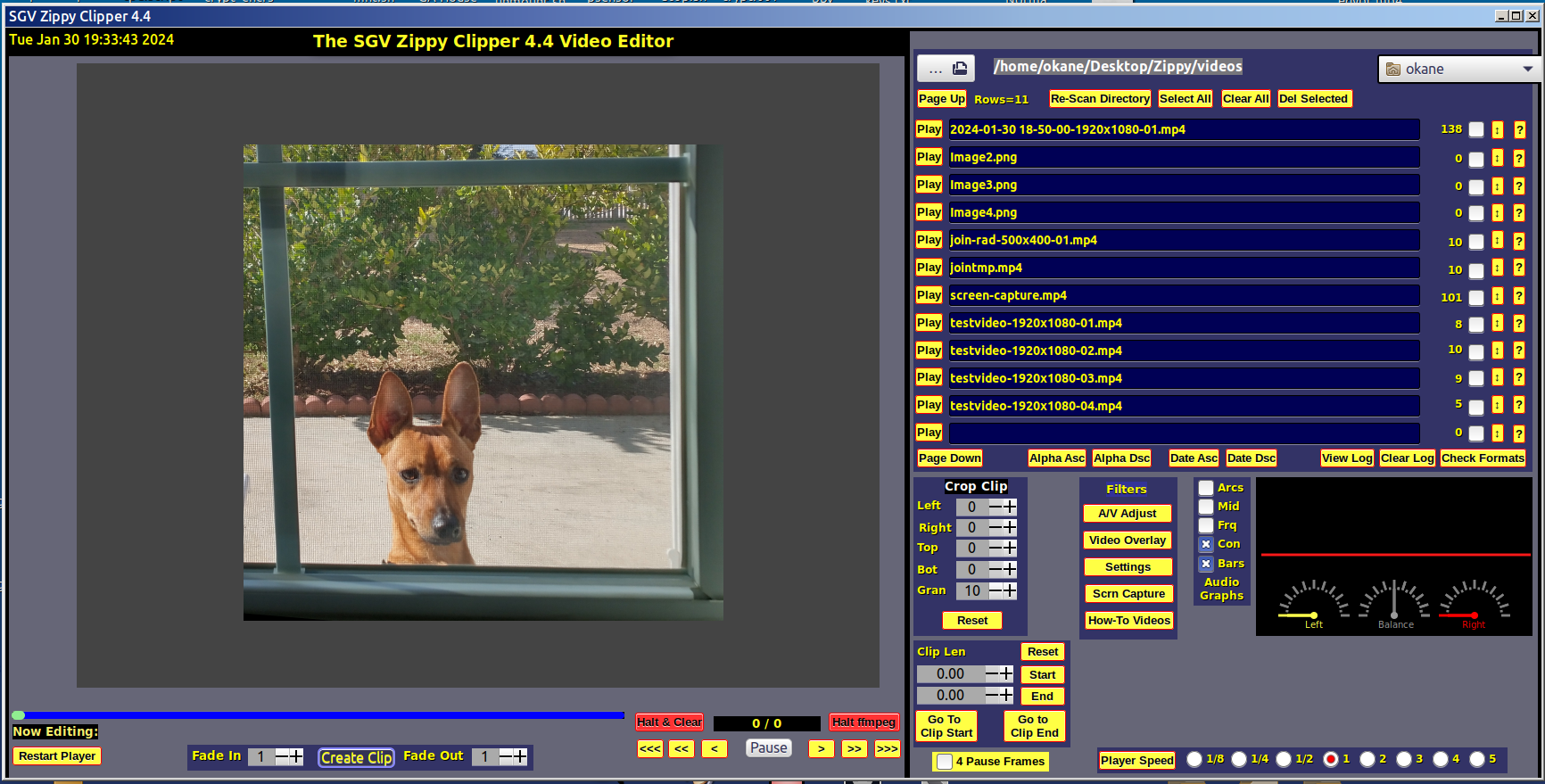
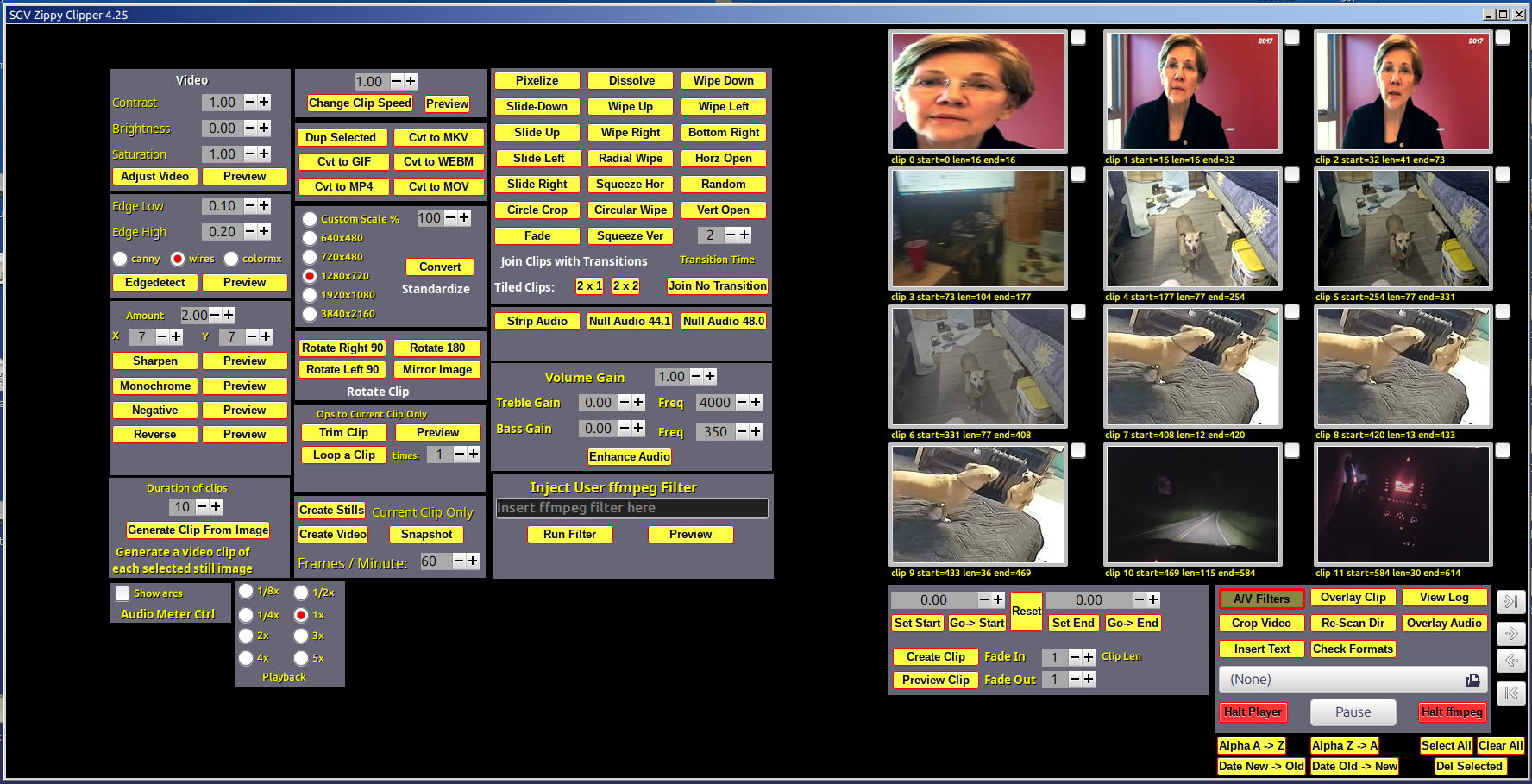
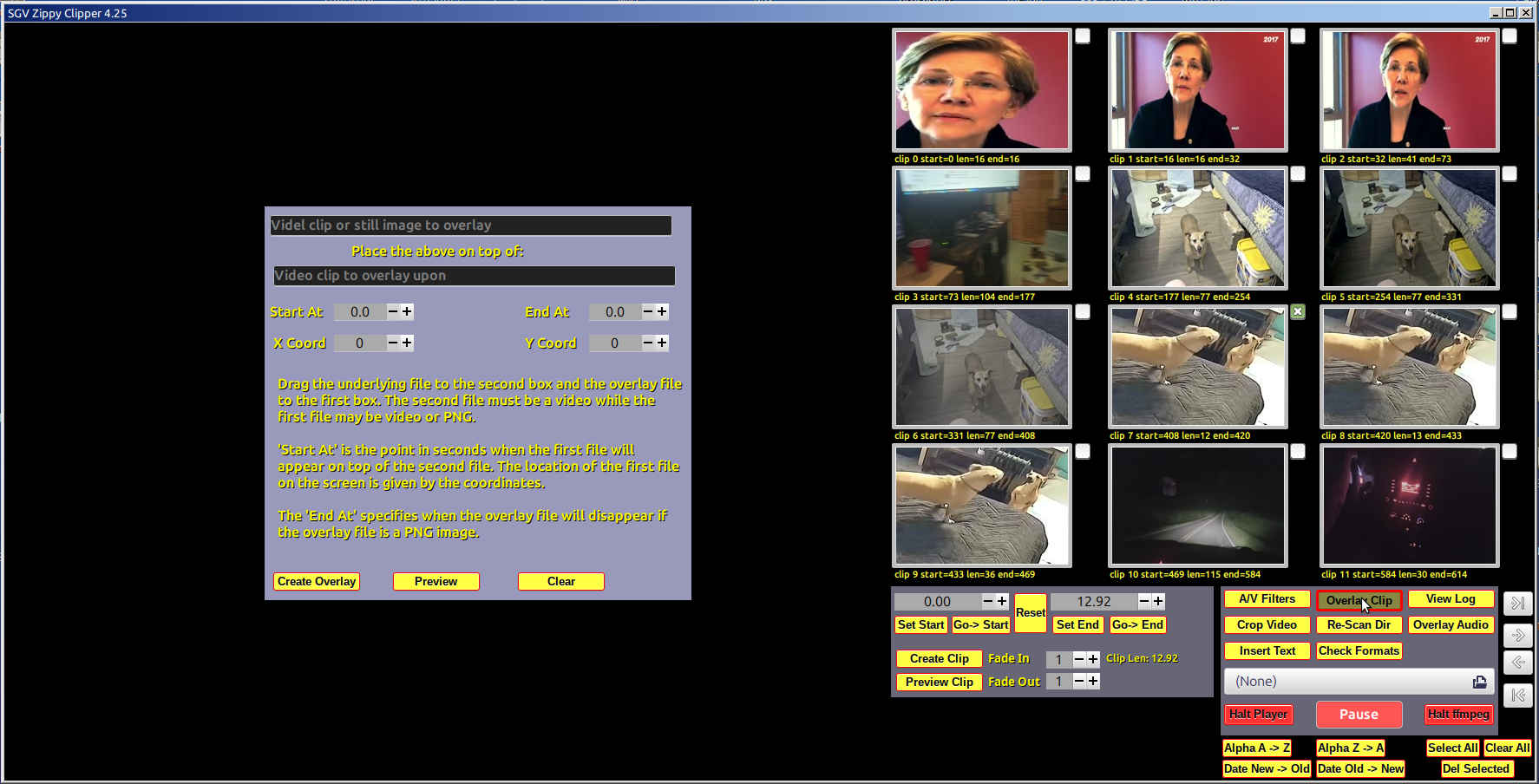
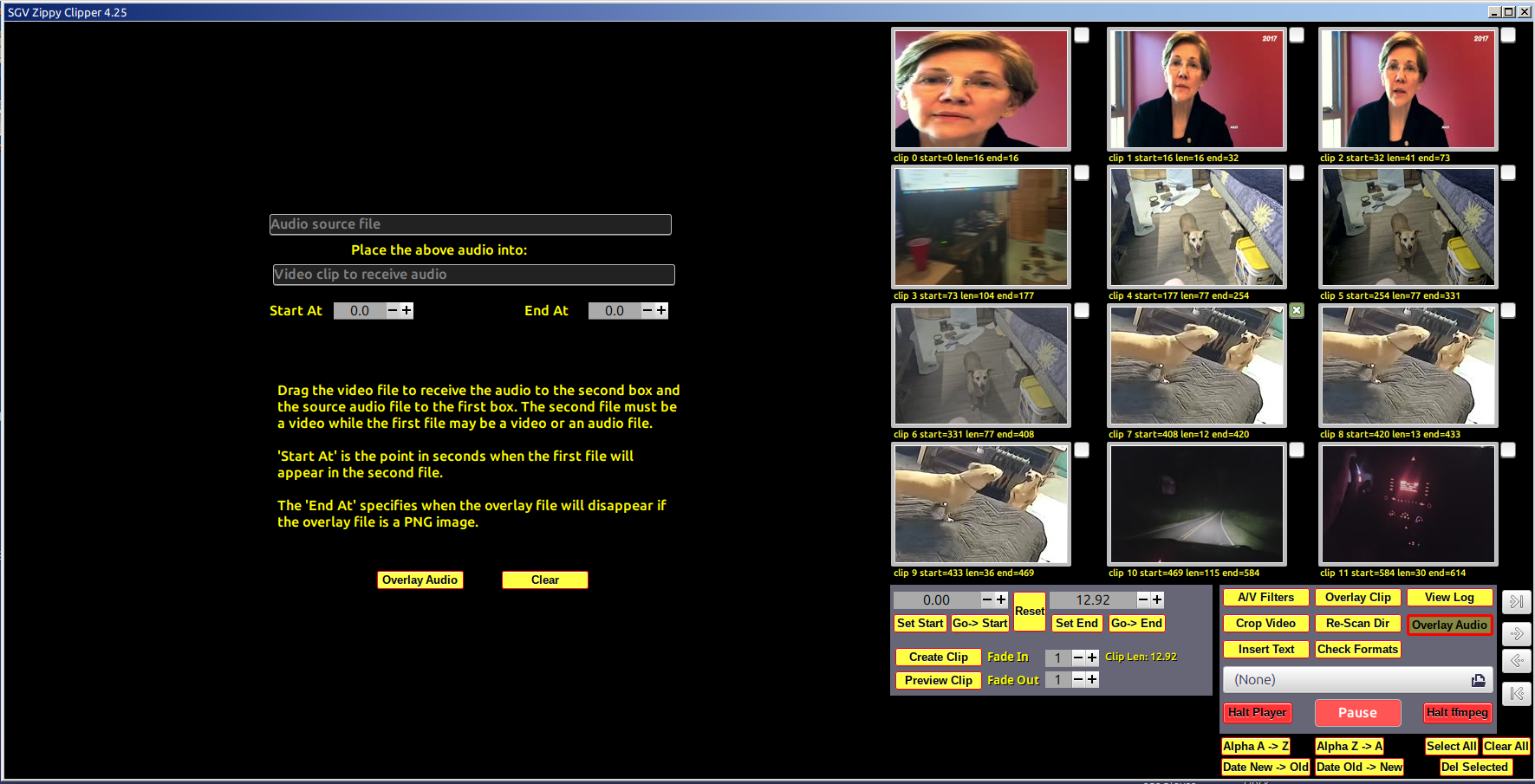
From Wikipedia: FFmpeg is a free and open-source software project consisting of a suite of libraries and programs for handling video, audio, and other multimedia files and streams. At its core is the command-line FFmpeg tool itself, designed for processing video and audio files. It is widely used for format transcoding, basic editing (trimming and concatenation), video scaling, video post-production effects, and standards compliance. Unfortunately, FFmpeg is, as noted, accessed as a command-line application with a sysntax that places it out of reach of most people. The purpose of this code is to introduce a graphical user interface front-end for several popular FFmpeg capabilities. The FFmpeg GUI is written in C and uses GTK 3, Glade, VLC libraries as well as FFmpeg and related code. The user selects files, settings and other options from the GUI and the code translates these into an FFmpeg command which is executed. For example, to join two video clips with a wipedown overlap, the GUI user selects two videos from a list by checking boxes and then clicking the wipedown button. This translates to something like this: ffmpeg -y -loglevel info -i "/home/okane/Desktop/Zippy/ videos/join-wdn-1280x720-01.mp4" -i "/home/okane/Desktop/Zippy/videos/ 2025-01-10 10-17-04.mkv" -filter_complex "[0v][1v]xfade=transition=wipedown :duration=2:offset=153.166000, format=yuv420p[video];[0:a][1:a]acrossfade=d=2: c1=tri:c2=tri[audio]; [video]fps=25[video1]" -map "[video1]" -map "[audio]" -movflags +faststart -c:a libopus -b:a 128k -c:v libx264 -preset veryslow -crf 20 "tmp.mp4" In this project, many common video operations have been encoded and more will be added. Suggestions welcome. The code is under development and seriously messy. Try not to look too carefully for style. There isn't any...
Notices The interface has been simplified and some content is hidden until requested. See the buttons in the box on the lower right of the main screen These cause other frames to appear/disappear. A new panel showing a frame from each video in a tiled arrangemnt is now available. Click the Video Tiles button on the main screen, center bottom. This will display the tiles page. You may drag/drop tiles as needed. Please click the Re-Scan Dir button to update the tiles, entry boxe and times when ever you add or seriously modify the contents of the video directory. This project is unaffiliated with FFmpeg. All errors, mistakes, and stupid code are mine alone. The HowTo videos are stored on a server in order to minimize the size of the distro and to permit updates as needed that can be seen by all. Clicking the HowTo button loads a list of URLs from the HowTo directory. You may play these in the Zippy Clipper directly if you have internet access. Click the Re-Scan Dir to restore access to local videos. The main development platform is Linux Mint with Mate. The present version of Mint is 22. The Mint X theme with WinMe borders. Other platforms are checked and updated when time allows. Due to systems update, etc., they may not all work at the same time. License and Acknowledgements: This code is licensed under the GPL 2+ & MIT licenses. The code uses FFmpeg runtime routines as well as VLC library APIs which themselves have various open source licences.
Examples:
The Linux version was developed on Linux Mint with Mate (21). It assumes library names and locations consistent with a Debian/Ubuntu based system. The installation script uses apt. Demo (co-starring Mabel) After |