Homework 10
Techniques for Building Scanners and Parsers
Out: Friday, October 10
Due: Monday, October 20, at 11:59 PM
Instructions
This assignment asks you to apply some of the techniques that we learned in class for constructing scanners and parsers. We applied them in class several times. This is a chance for you to refresh your memory and try them again.
You may refer to your personal notes and to the courses notes online while doing your work. Each problem links to a page or two that cover the technique in question. You may also ask me for help!
Tasks
Problem 1
Consider this regular expression: b(a|b)*a
In class, we learned that we could create an equivalent NFA by walking down the expression character by character:
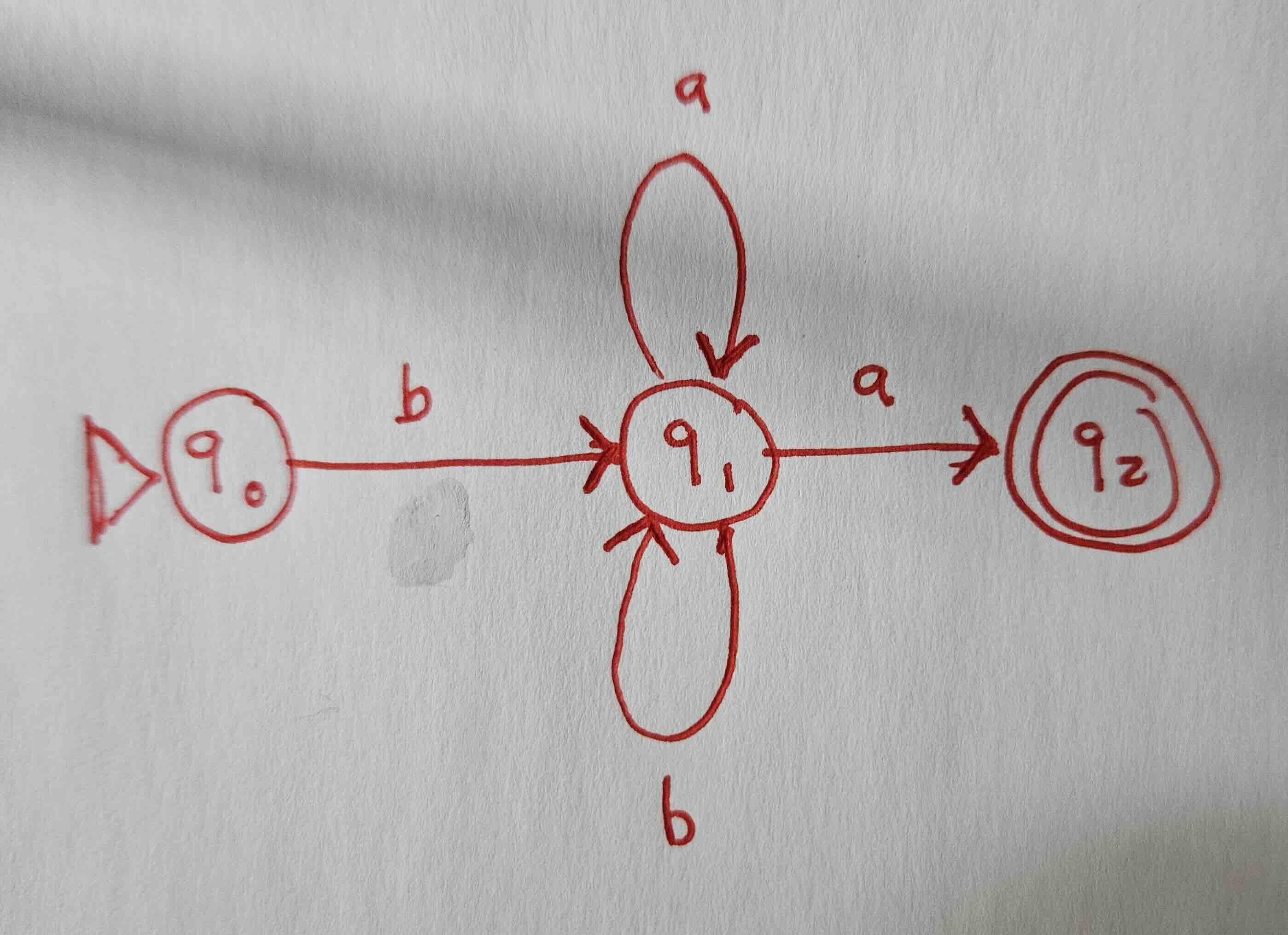
Use the technique we learned in class to convert this NFA into an equivalent DFA, by simulating the NFA on all possible inputs.
Problems 2 through 5
A Grammar
Use this grammar for the next four problems:
statement := for identifier in list-of-terms do statement
| identifier := binary-expr
list-of-terms := ( term rest-of-list )
rest-of-list := , term rest-of-list
| ε
binary-expr := term op term
term := identifier
| number
identifier, number, and op are terminals, as are these keywords and operators:
for in do := ( , )
Problem 2
Define the abstract syntax for this grammar.
Problem 3
Define the FIRST and FOLLOW sets for the grammar.
Problem 4
Use your FIRST and FOLLOW sets to create the top-down parsing table for this grammar.
Problem 5
Use your parsing table to trace the operation of a table-driven parser as it recognizes this token stream:
for i in (1, x) do
j := j * i
Deliverables
By the due time and date, submit your assignment in one of two ways:
-
Use
the course submission system
to submit digital files.
You may submit the text answers in PDF or plain text.
You may submit the DFA for Problem 1 as a JPG or PNG file. -
Turn your answers in on paper.
Bring the hard copy to class, or deliver it to the department office, CEEE 015.