Study Questions Exam IV
Angiosperms
1. omit
2. Angion is greek for_______________.
3. About how many species of angiosperms?
4. What are the four major parts of a flower that are derived from specialized leaves?
5. What's a fruit?
6. What's a fruit good for?s
7. Why does a strawberry turn red?
8. omit
9. The male part of a flower is the___________ and has an_________ on top of a ________.
10. What are the parts of a carpel?
11. omit
12. What's an anachronistic fruit!?
13. Janzen would say that hedge apples and/or Guanacaste fruits are becoming more rare because
_____________ are missing.
14. What does dioecious mean?
15. Know your parts of the angiosperm life-cycle: names and
ploidy and what makes what. Megasporangium, megaspore, microsporangium
microspore, central cell, double fertilization, endosperm, female
gametophyte, male gametophyte. What ploidy level are they? n, 2n
or 3n?
16. What's a micropyle?
17. What is corn silk?
18. What's the difference between monocots and eudicots?
20. What is coevolution?
UNIKONTS
1. What are the two clades within Unikonta?
2. The fusion of the DHFR and TS genes means what for the phylogeny of Eukaryotes? 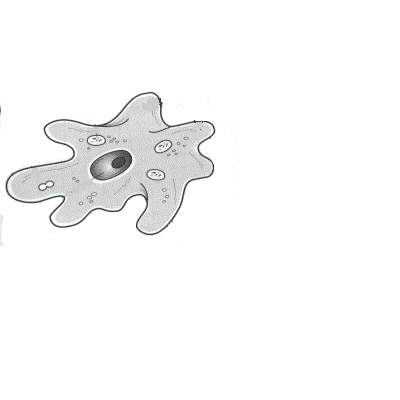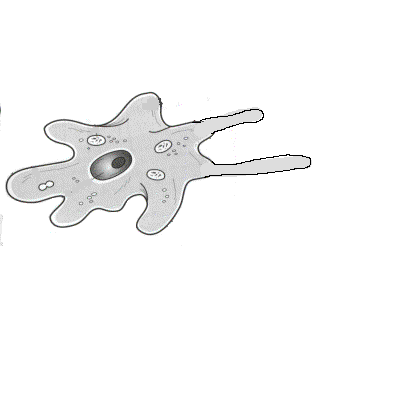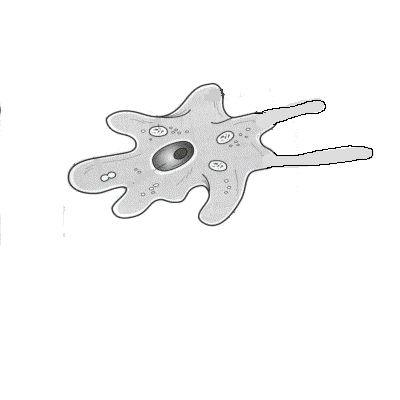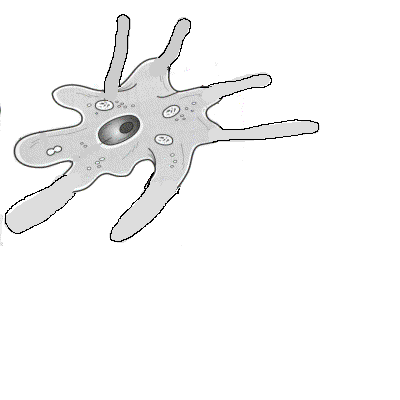
3. What are the three groups of amoebozoans?
4. Describe the two types of slime molds.
5. Describe the life cycle of a cellular slime mold.
6. Why not cheat all the time and avoid being a stem?
7. Gymnamoebas live where?
8. Entamoebas live where?
9. What are some diseases that entamoebas cause?
10. What does opisthokont mean - literally?
11. How many times has multicellularity evolved in the opisthokonts? (look at the tree!)
12. Draw, label and describe a general life cycle for a fungus.
13. What are the two types of mycorrhizae? How do they differ?
14. Cell walls of fungus are made of__________.
15. What are haustoria?
16. What is heterotrophy?
17. What happens during plasmogamy?
18. Karyogamy?
19. What's a mold?
20. What's a yeast?
21. What are Chytrids and how do they get nutrition?
22. What is a zygomycete? Give an example.
23. What is Pilobolus? Why do they face light?
24. What is a glomeromycete? Why are they important? What type of mycorrhizae do they form?
25. Describe the reproductive structures of ascomycetes.
26. What are three "good" ascomycetes?
27. What is a sac fungi?
28. How can ascomycetes get their nutrition?
29. Beer has been aroound for ____ years.
30. _____________ discovered penicillin in what year?
31. What is Fusarium, Cryptococcus, Ergot and Candida? Be specific.
32. Claviceps infects_____________ and produces 4 alkaloids:
33. Describe how Cordyceps can effect an ant's behavior and why.
bat
34. To what group of fungi does White-nose Syndrome belong?
35. Basidiomycetes are called __________fungi because of the shape of the _______________.
36. Basidomycetes and_________________ are sister taxa.
37. One common name for a basidiocarp is _____________.
38. If examined closely, you may be able to find 3 different
nuclear arrangements in the basidiocarps on your pizza. What are
they?
39. Know the life cycle of a basidiomycete!
40. What's a lichen?
41. What are leaf-cutter ants doing?
42. What's an endophytic fungus?
43. Be able to match the member (Parabasalid, Red Algae etc.) to
the appropriate eukaryotic super group. Imagine a matching
question with the five super groups as choices and the examples
on the tips of the tree being questions. You just need to match
the example to one of the five super groups. Use your tree
diagram hand out.
44. Classify thy self. Domain, Supergroup, Kingdom, Phylum,
Class, Order, Genus, and Species (remember the rule on species names!).
45. How do leaf-cutter ants control the parasitic fungi that attack their fungal crops?
46. With respect to cell structure and function, what are the four main characteristics of animals?
47. Describe animal development from egg to gastrula.
48. What is a Hox gene and who has them?
49. What are the choanoflagellates and what two bits of data tell us that they are similar to the ancesator of animals?
50. What are these and in what order did they occur?: Paleozoic, Mesozoic, Cenozoic, Neoproteozoic.
51. In which of the above did mammals arise?
52. What are the two types of symmetry and how might they aid in the evolution of complexity?
53. What are the three germ layers and what do they give rise to?
54. A true coelem is lined with tissue from ____________________.
55. What are the differences between protostome and deuterostome development?
56. Know your phylogeny of the animal handout. Know the
major groups (in the boxes) and the placement of the taxa with
stars, Silicea, Calcarea, Echinodermata, Chordata,
Platyhelminthes, Mollusca, Nematoda, Arthropoda.
FINAL EXAM IS ON TUESDAY AT 10AM!!!!!!!!!!
Want to re-live the wonder and excitement of one of my recent lectures
in the comfort of your own dorm room? Want to amaze, perplex, or
gross-out your non-biology roomates? Or may be you even want to
re-check something before the final? Check out these self-pirated
versions of my presentations:
Unikont (overview)
Fungus!
Animals I
